Everything You Need to Know About Pap Smears
Regular Pap smears are essential for maintaining women’s reproductive health. This simple screening method plays a huge role in preventing cervical cancer, a disease that affects thousands of women annually.
In his article, we will help women between the ages of 18 and 60 understand the importance of regular Pap smears, how they work, and why they are necessary for long-term health.
A Pap smear is a procedure where cells are collected from the cervix and examined for any precancerous or cancerous changes. The test is noninvasive and takes just a few minutes, but it has the potential to save lives. For women aged 18 to 60, this screening is vital in catching cervical cancer at an early stage, where treatment is most effective.
What is a Pap Smear?
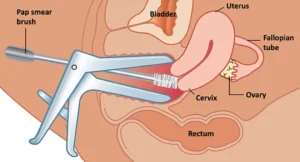
A Pap smear, also known as a Pap test, is a procedure designed to screen for cervical cancer and detect changes in the cervical cells that may lead to cancer in the future. It is a routine test conducted during a gynecological exam. During the procedure, your doctor will use a small spatula or brush to collect a sample of cells from the cervix, which is then sent to a laboratory for analysis. This test identifies any abnormalities in the cells, including infections or precancerous changes, that could potentially develop into cancer if left untreated.
According to international guidelines, women aged 21 to 29 should get a Pap smear every three years. For women between 30 and 65, it’s recommended to get a Pap smear along with HPV testing every three to five years. However, women with previous abnormal results, weakened immune systems, or other health concerns may need to be tested more frequently. Regular screening ensures that cervical cell changes are detected and treated promptly.
Importance of Regular Pap Smears
Cervical cancer is one of the most preventable types of cancer if caught early. Women who regularly undergo Pap smears have a significantly higher chance of detecting cervical cancer in its early stages when it is most treatable and manageable. Early detection allows for more straightforward and less invasive treatment options, leading to better outcomes.
Another essential benefit of regular Pap smears is their ability to detect precancerous changes in the cervical cells. These changes, if left untreated, can develop into cancer over time. Treating these abnormalities early on can prevent the progression of the disease. Additionally, routine screenings have played a significant role in reducing cervical cancer mortality.
In countries with good screening programs, cervical cancer death rates have dropped by more than 70%. This reduction in mortality highlights the lifesaving potential of regular Pap smears. By staying on top of their screening schedule, women can take control of their health and reduce their risk of cervical cancer significantly.
The Link Between HPV and Cervical Cancer
Human Papillomavirus (HPV) is the leading cause of cervical cancer, making its connection to regular Pap smears essential to understand. HPV is a common sexually transmitted infection, and while most HPV infections clear up on their own, certain strains can lead to cervical cancer if they persist. Almost all cases of cervical cancer are linked to HPV, which is why Pap smears play a critical role in detecting abnormalities caused by the virus.
Pap smears can identify early cellular changes caused by HPV before they develop into cancer, allowing doctors to monitor and treat any abnormalities early. In addition, many Pap smears now include HPV testing, which helps doctors determine whether a woman has contracted a highrisk strain of the virus. While the HPV vaccine is available and offers excellent protection against the most dangerous strains of the virus, it is not a substitute for regular Pap smears.
What to Expect During a Pap Smear
The idea of getting a Pap smear can be nerve-wracking, but understanding the process can help alleviate some of that anxiety. Preparing for a Pap smear involves avoiding sexual intercourse, douching, or using vaginal creams for at least 48 hours before the test. These activities can interfere with the accuracy of the test results by washing away or hiding abnormal cells.
During the procedure, you will lie on an exam table with your feet in stirrups while your doctor inserts a speculum into the vagina to gently widen it, allowing them to access the cervix. Using a small spatula or brush, the doctor will then collect a sample of cells from the cervix. The procedure may feel slightly uncomfortable or cause pressure, but it is usually painless and very quick, typically lasting only a few minutes.
After the Pap smear, you can resume your regular activities immediately. Results usually take a few days to a week, depending on the lab’s processing time. If the results are normal, you will continue with regular screening as recommended by your healthcare provider. If the results show abnormalities, your doctor will explain the next steps, which may involve further testing or follow-up procedures.
Common Myths and Misconceptions About Pap Smears
There are several myths and misconceptions about Pap smears that can prevent women from getting tested regularly.
One common myth is that Pap smears are painful. While the procedure may cause some mild discomfort due to the insertion of the speculum, it should not be painful. Most women report feeling only slight pressure or a brief pinch. Addressing this misconception is vital in encouraging more women to get tested without fear of pain.
Another misconception is that Pap smears are unnecessary if you feel healthy. Whereas in reality cervical cancer and precancerous changes often have no symptoms in their early stages. By the time symptoms appear, the cancer may have progressed to a more advanced and less treatable stage.
Furthermore, some women believe that if they’ve had a hysterectomy, they no longer need Pap smears. This depends on the type of hysterectomy and the reason for the surgery. If the cervix was not removed, or if the hysterectomy was performed due to cancer or precancerous changes, regular Pap smears may still be necessary.
What Happens if You Have an Abnormal Pap Smear?
Receiving an abnormal Pap smear result can be concerning, but it does not necessarily mean you have cancer. In many cases, an abnormal result simply means that there are changes in the cervical cells that need to be monitored or treated. Some common types of abnormalities include ASCUS (atypical squamous cells of undetermined significance), LSIL (lowgrade squamous intraepithelial lesion), and HSIL (highgrade squamous intraepithelial lesion). These terms refer to the severity of the changes in the cervical cells.
If your Pap smear results are abnormal, your doctor may recommend further testing, such as a colposcopy or biopsy. A colposcopy is a procedure where your doctor uses a special magnifying instrument to closely examine your cervix for abnormal areas. If necessary, a small sample of tissue may be taken for a biopsy to determine whether the abnormal cells are precancerous or cancerous.
Depending on the results of these follow-up tests, treatment options may include cryotherapy (freezing the abnormal cells), LEEP (loop electrosurgical excision procedure), or monitoring the cells with repeat Pap smears. Treating precancerous cells early can prevent them from progressing into cancer, highlighting the importance of follow-up care after an abnormal Pap smear result.
Barriers to Getting Regular Pap Smears
Despite the importance of regular Pap smears, many women face barriers such as anxiety, lack of awareness, etc that prevent them from getting screened regularly.
- Fear and Anxiety are some of the biggest barriers. Some women may worry about discomfort or feel embarrassed about the exam. Addressing these concerns with accurate information about what to expect during the test can help ease anxiety.
- Lack of Awareness is why many women don’t understand the importance of regular Pap smears, especially if they feel healthy or are not sexually active.
- Accessibility is another issue that can prevent women from getting regular Pap smears. The cost of the test, lack of health insurance, or difficulty accessing healthcare facilities can all pose challenges. Fortunately, many clinics and health programs offer free or low-cost Pap smears to women who cannot afford the test.
Regular Screenings: How to Stay On Track
Staying on top of your Pap smear schedule is key to ensuring you remain proactive about your health. One of the easiest ways to stay on track is to schedule your Pap smear around other annual health checkups. Many women find it convenient to sync their screenings with annual physicals or gynecological exams.
Setting reminders on your phone or calendar can also help you remember when it’s time for your next Pap smear.
Some healthcare providers send reminder letters or text messages to inform you when your screening is due. Staying in regular communication with your healthcare provider is essential for discussing your personal risk factors and determining the appropriate screening schedule.
Conclusion
Regular Pap smears are extremely important for women’s health. They offer a simple way to detect cervical cancer and other abnormalities early on. For women between the ages of 18 and 60, Pap smears should be a part of routine check up.
If you fall within this age group, now is the time to take action and speak with your doctor about scheduling a Pap smear.
At Frontline, our team of experts helps make the process as comfortable as possible for you while maintaining the international standards at the same time, book your appointment now!